Delayed booster dosing improves human antigen-specific Ig and B
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 abril 2025

medRxiv - The Preprint Server for Health Sciences
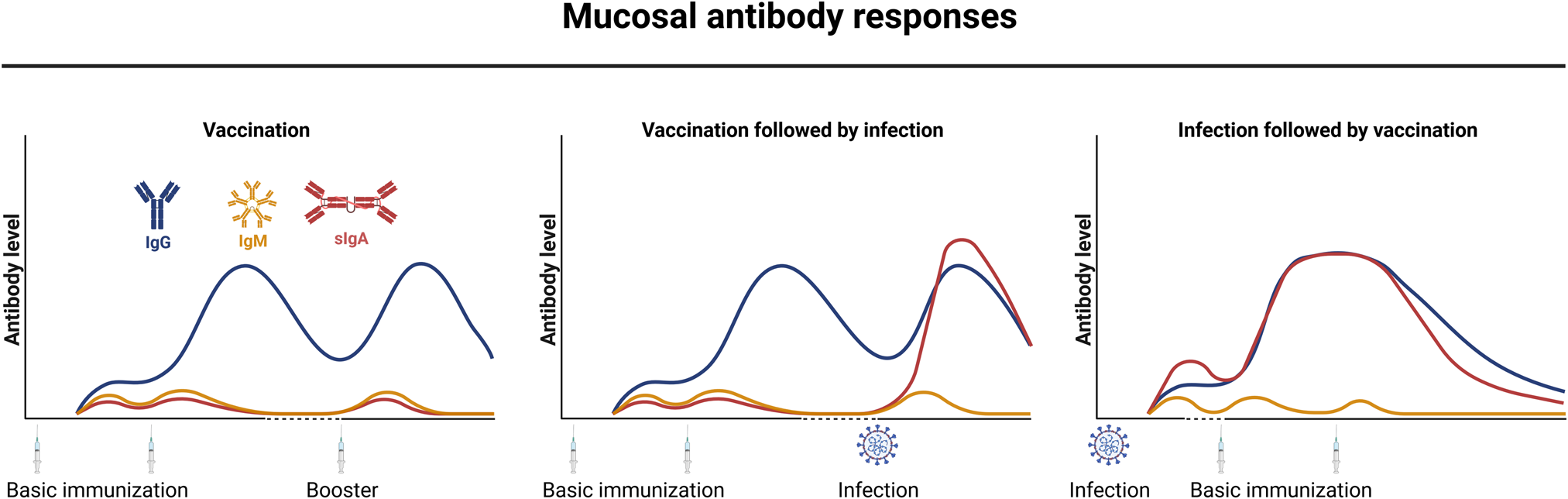
B-cell and antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2: infection, vaccination, and hybrid immunity

Beta-spike-containing boosters induce robust and functional antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in macaques primed with distinct vaccines - ScienceDirect

Persistence and post-antigen recall responses of HBsAg-specific

Peptides for Vaccine Development

Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals after mRNA vaccination
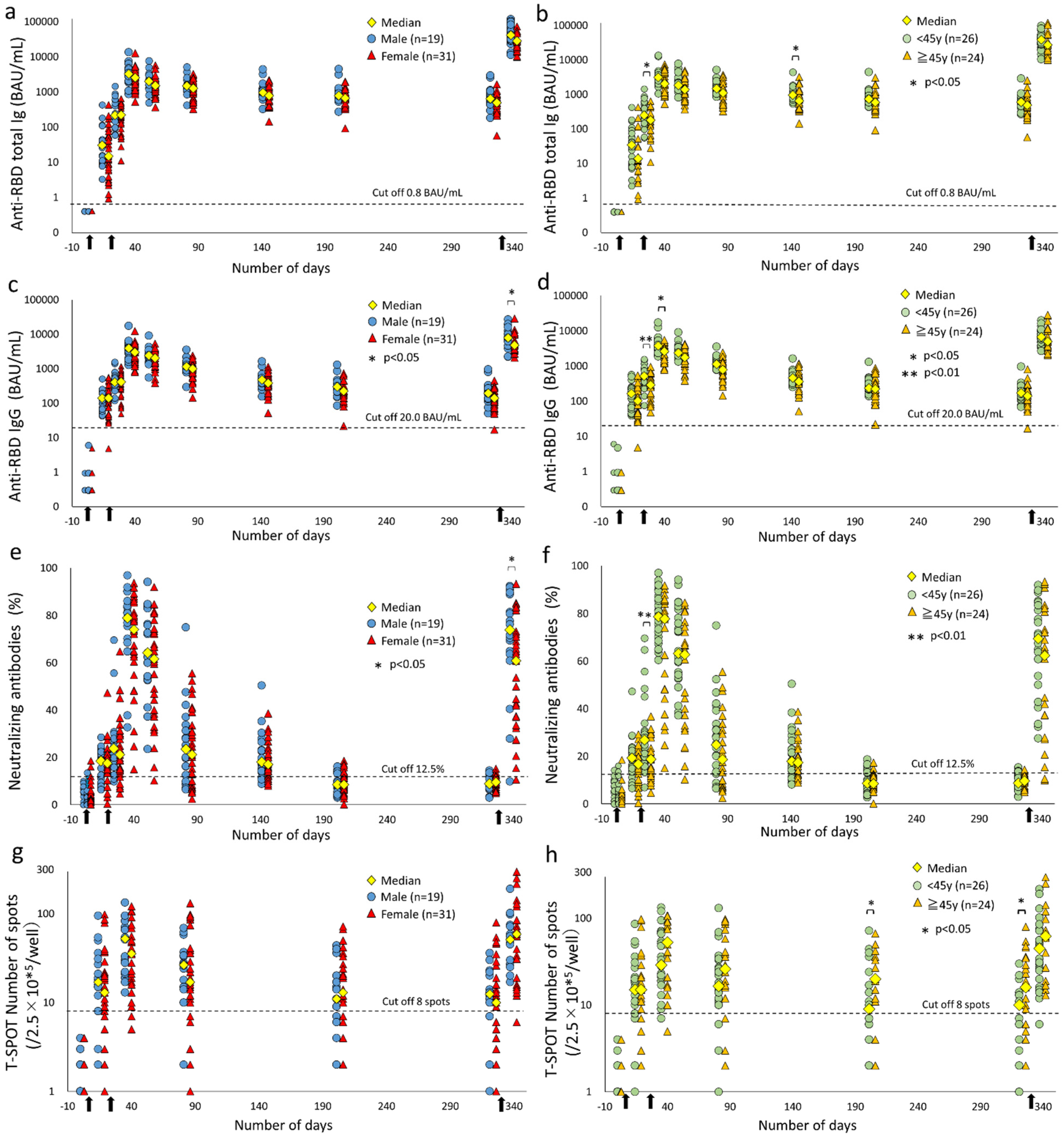
Vaccines, Free Full-Text

Delayed booster dosing improves human antigen-specific Ig and B cell responses to the RH5.1/AS01B malaria vaccine
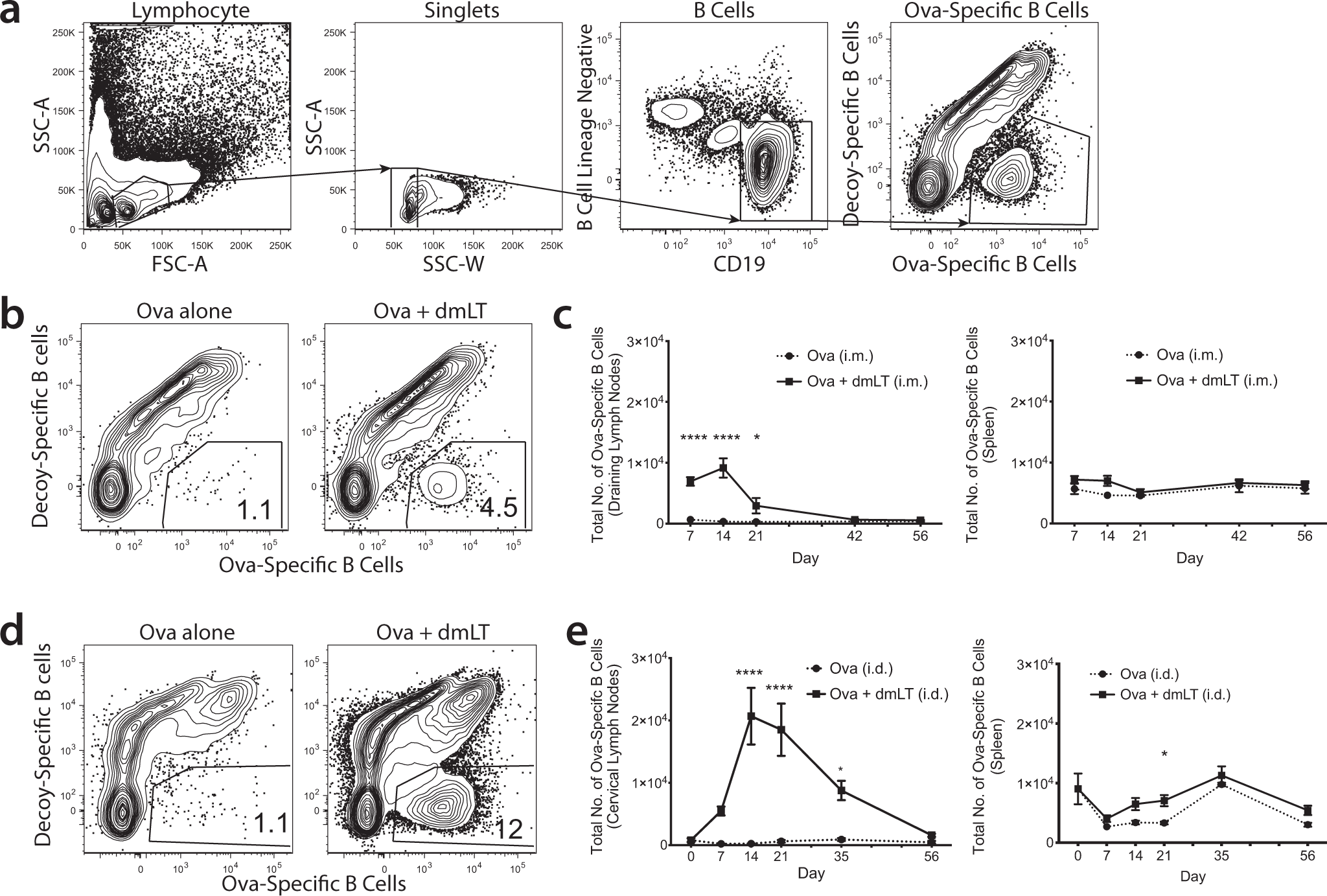
Establishment of isotype-switched, antigen-specific B cells in multiple mucosal tissues using non-mucosal immunization

Cureus, Dynamic Antibody Response and Hybrid Immunity Following Multiple COVID-19 Vaccine Doses and Infection: A Case Study
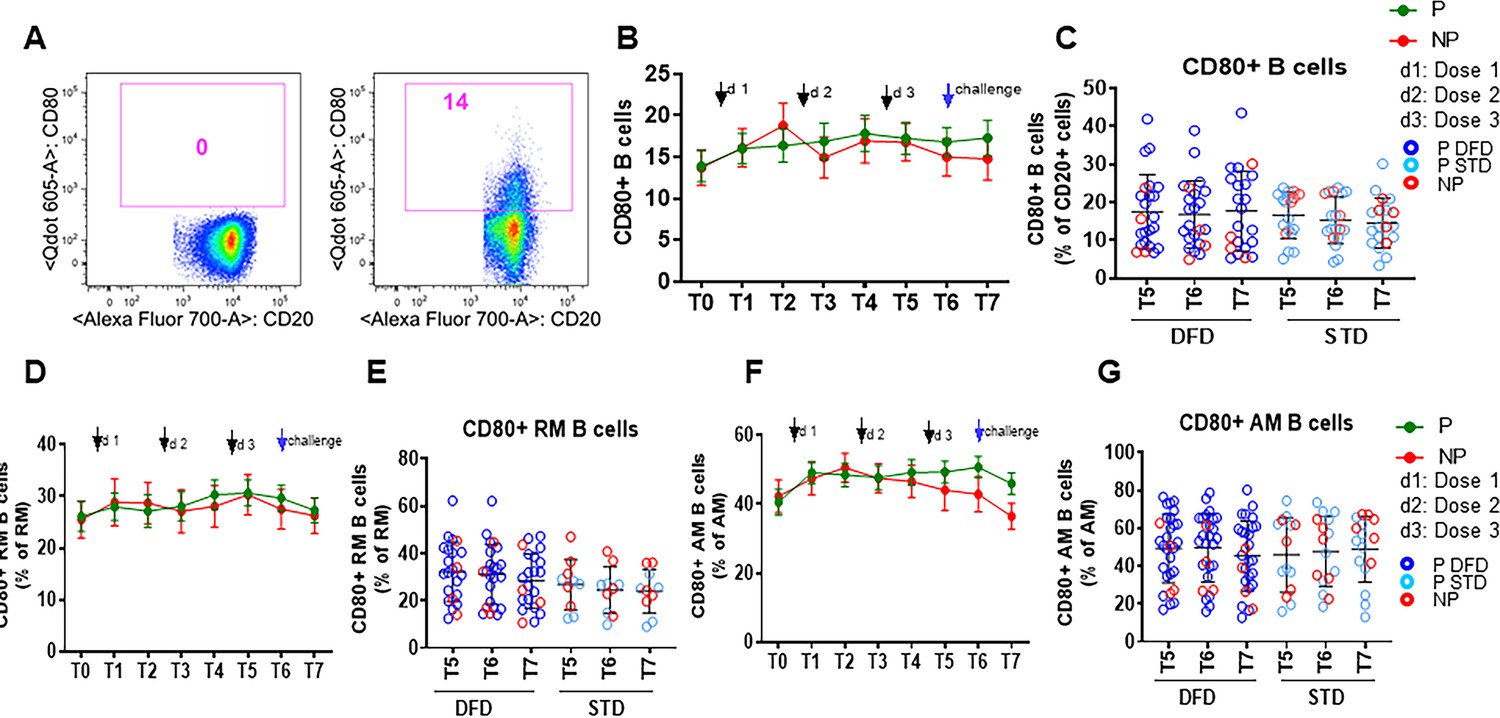
A delayed fractionated dose RTS,S AS01 vaccine regimen mediates protection via improved T follicular helper and B cell responses
Recomendado para você
-
 Shotgun King: The Final Checkmate Free Download (v1.39c) « IGGGAMES06 abril 2025
Shotgun King: The Final Checkmate Free Download (v1.39c) « IGGGAMES06 abril 2025 -
 Fetal genome profiling at 5 weeks of gestation after noninvasive06 abril 2025
Fetal genome profiling at 5 weeks of gestation after noninvasive06 abril 2025 -
 Transcriptional and clonal characterization of B cell plasmablast06 abril 2025
Transcriptional and clonal characterization of B cell plasmablast06 abril 2025 -
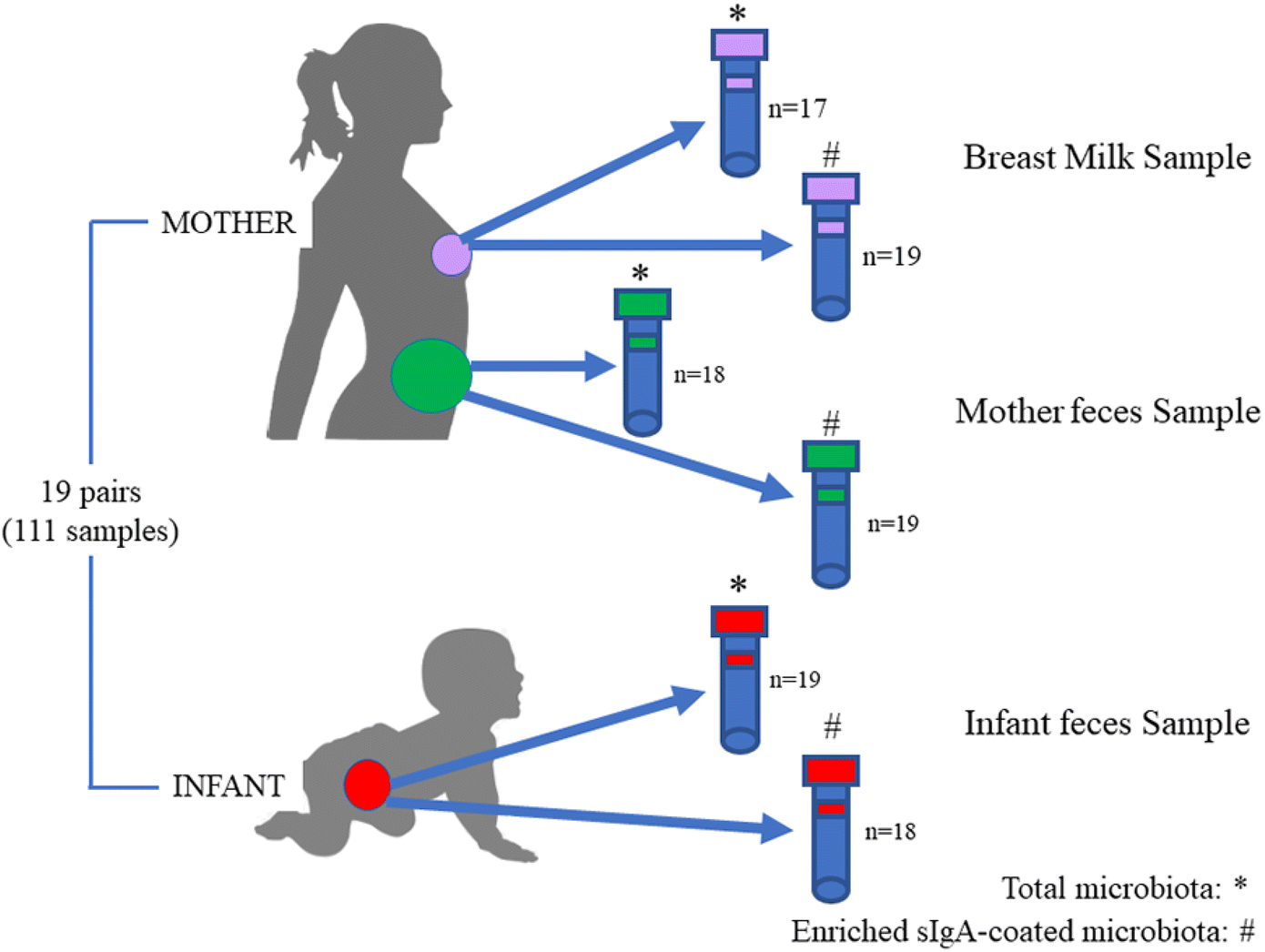 Widespread vertical transmission of secretory immunoglobulin A06 abril 2025
Widespread vertical transmission of secretory immunoglobulin A06 abril 2025 -
 Quantitative Recoveries of Exosomes and Monoclonal Antibodies from06 abril 2025
Quantitative Recoveries of Exosomes and Monoclonal Antibodies from06 abril 2025 -
C&Rsenal06 abril 2025
-
 Gut microbiota‐derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel06 abril 2025
Gut microbiota‐derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel06 abril 2025 -
 Dynamic interactome of the MHC I peptide loading complex in human06 abril 2025
Dynamic interactome of the MHC I peptide loading complex in human06 abril 2025 -
 Augmented Binary Substitution: Single-pass CDR germ-lining and06 abril 2025
Augmented Binary Substitution: Single-pass CDR germ-lining and06 abril 2025 -
 The G2 phase controls binary division of Toxoplasma gondii06 abril 2025
The G2 phase controls binary division of Toxoplasma gondii06 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Photon Tournament-SDK - Real-time, eSports-style events inside your games06 abril 2025
Photon Tournament-SDK - Real-time, eSports-style events inside your games06 abril 2025 -
 Cute Cat Kitten Bite GIF - CuteCat KittenBite BiteMyLip - Discover06 abril 2025
Cute Cat Kitten Bite GIF - CuteCat KittenBite BiteMyLip - Discover06 abril 2025 -
 News - Pre-Purchase Now - NBA 2K1506 abril 2025
News - Pre-Purchase Now - NBA 2K1506 abril 2025 -
 AMVeSAIMOE: Os melhores animes da Temporada de Verão 201306 abril 2025
AMVeSAIMOE: Os melhores animes da Temporada de Verão 201306 abril 2025 -
![self] Simon “Ghost” Riley MW2019 : r/cosplay](https://i.redd.it/amxcad2bb8t71.jpg) self] Simon “Ghost” Riley MW2019 : r/cosplay06 abril 2025
self] Simon “Ghost” Riley MW2019 : r/cosplay06 abril 2025 -
 HOLD THE LINE (TRADUÇÃO) - Avicii06 abril 2025
HOLD THE LINE (TRADUÇÃO) - Avicii06 abril 2025 -
 Three youngsters cross 2700 mark in September rating list06 abril 2025
Three youngsters cross 2700 mark in September rating list06 abril 2025 -
 PPT - EIS-ME AQUI Letra e Música: Ana Paula Valadão PowerPoint Presentation - ID:514891106 abril 2025
PPT - EIS-ME AQUI Letra e Música: Ana Paula Valadão PowerPoint Presentation - ID:514891106 abril 2025 -
 Premium Vector Anime girl sits in a half turn and poses for the camera on her skirt06 abril 2025
Premium Vector Anime girl sits in a half turn and poses for the camera on her skirt06 abril 2025 -
![DISC] Tensura Nikki - Tensei Shitara Slime Datta Ken Chapter 53 : r/manga](https://external-preview.redd.it/YfF4mSIejip5a4KPRkh3nK6dxI5qSTFHQpHYrcdn124.jpg?width=640&crop=smart&auto=webp&s=c64d0fc93b56a73cee3142d9edbb52d6c0471344) DISC] Tensura Nikki - Tensei Shitara Slime Datta Ken Chapter 53 : r/manga06 abril 2025
DISC] Tensura Nikki - Tensei Shitara Slime Datta Ken Chapter 53 : r/manga06 abril 2025
