Either roll two dice or simulate the rolling of two dice 100 times. Record the outcomes and calculate the empirical probabilities for all the possible outcomes.
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 05 abril 2025


Probability Distribution - Sum of Two Dice

Example 3 - A die is thrown 1000 times with frequencies - Examples
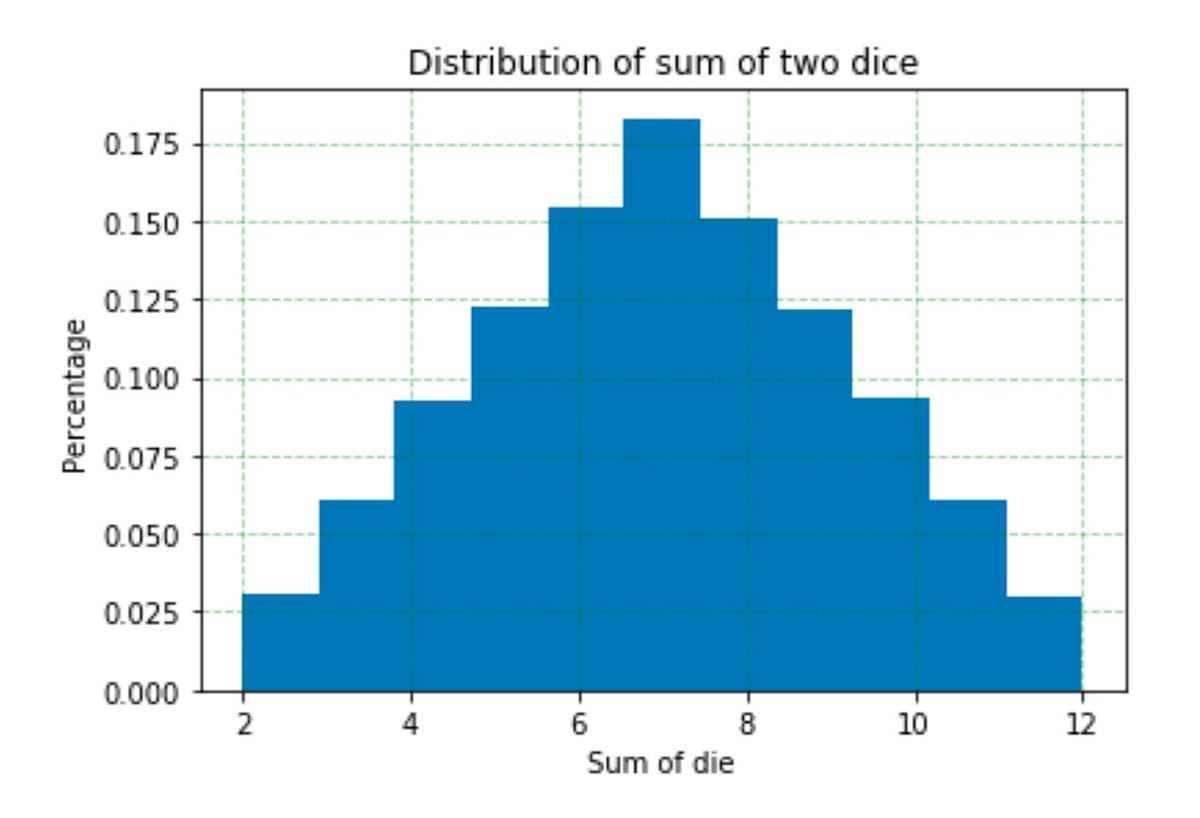
Simulating probability events in Python
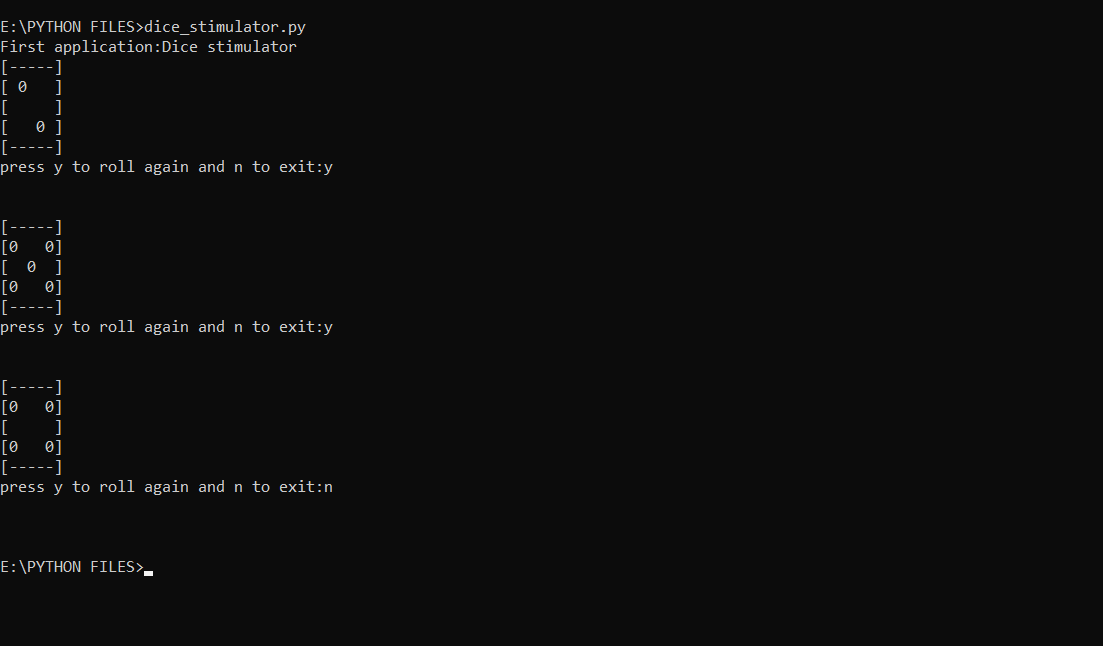
Dice Rolling Simulator using Python-random - GeeksforGeeks

Suppose that two fair dice are rolled and that the two numbe

Matemáticas: Simple and Compound Probability

Chapter 1 Discrete Probability Distributions - Dartmouth College
Mark rolls a fair die 36 times. How many times would Mark expect
The Monty Hall Problem: A Statistical Illusion - Statistics By Jim

probability - The expected payoff of a dice game - Mathematics

Solved 14. Inquiry/Problem Solving a) What are the possible
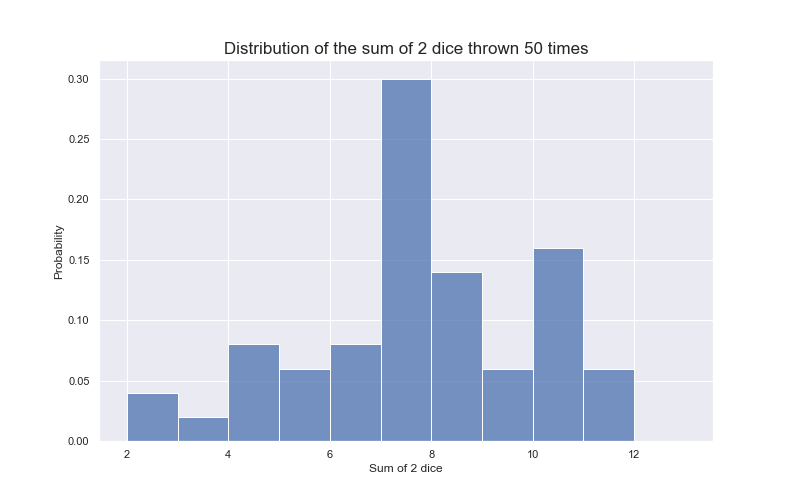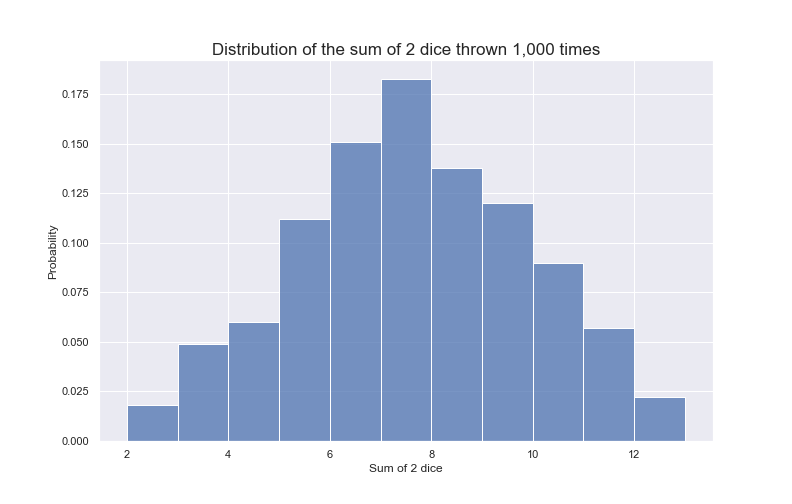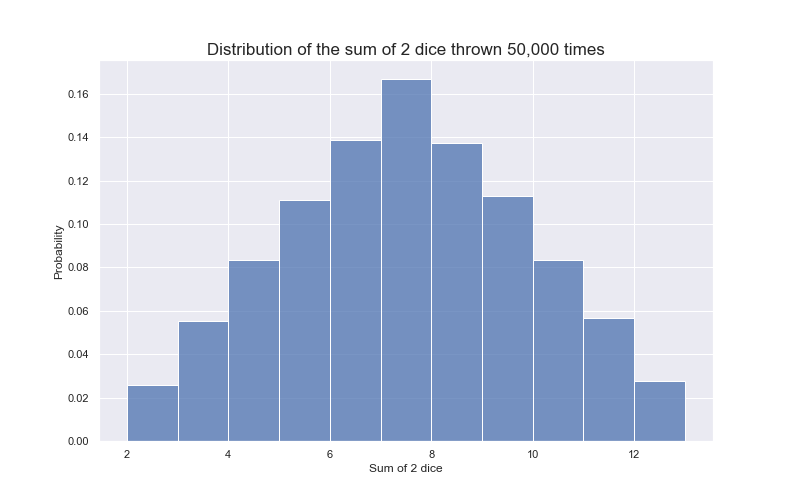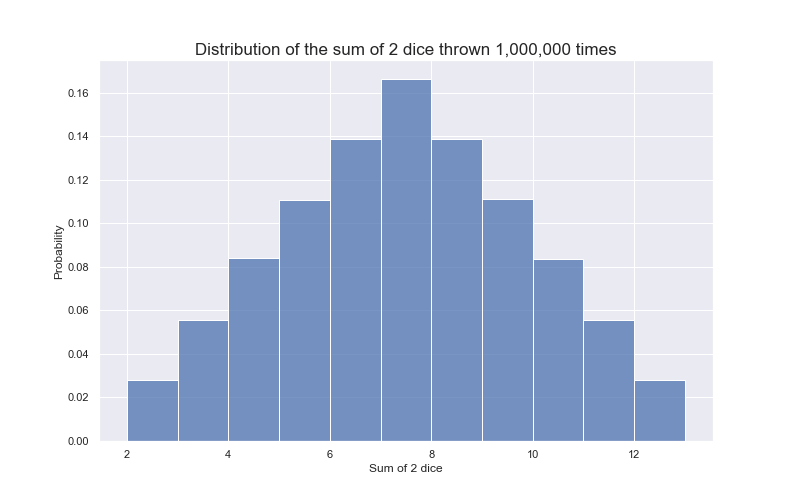
What to Expect when Throwing Dice and Adding Them Up
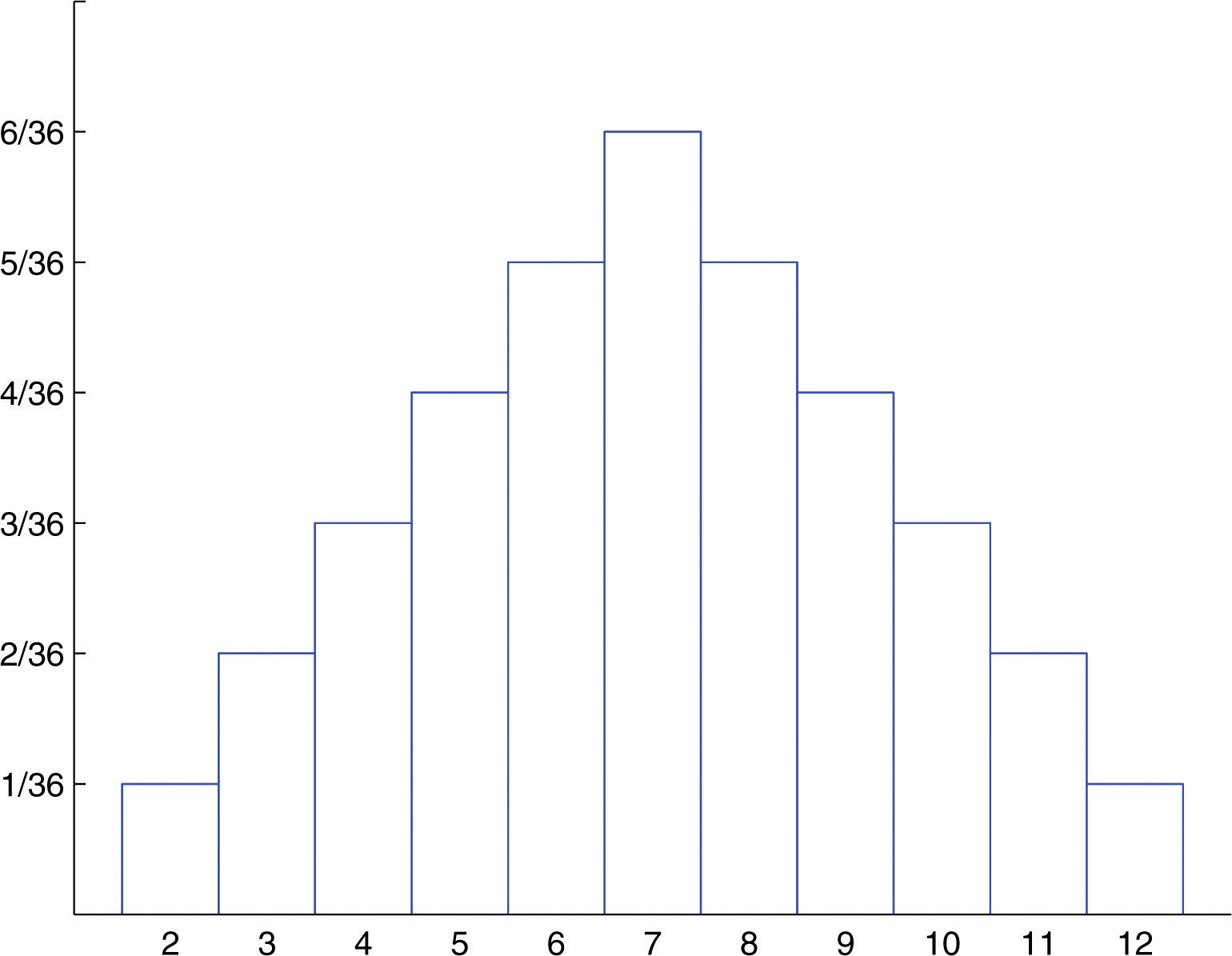
Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables
Recomendado para você
-
 20 Dice Games for Math, Reading, Art, and Fun! - WeAreTeachers05 abril 2025
20 Dice Games for Math, Reading, Art, and Fun! - WeAreTeachers05 abril 2025 -
 An Empirical Approach to Dice Probability – A Best-Case Scenario05 abril 2025
An Empirical Approach to Dice Probability – A Best-Case Scenario05 abril 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TwoDice-58bddad45f9b58af5c4aa0d4.jpg) Probabilities for Rolling Two Dice05 abril 2025
Probabilities for Rolling Two Dice05 abril 2025 -
What is the average roll with two dice? - Quora05 abril 2025
-
 probability - What is the average of rolling two dice and only05 abril 2025
probability - What is the average of rolling two dice and only05 abril 2025 -
 Digital Dice Google Classroom Roll 205 abril 2025
Digital Dice Google Classroom Roll 205 abril 2025 -
 Die (2), Spelunky Wiki05 abril 2025
Die (2), Spelunky Wiki05 abril 2025 -
 Roll and Cover Games for One and Two Dice - JDaniel4s Mom05 abril 2025
Roll and Cover Games for One and Two Dice - JDaniel4s Mom05 abril 2025 -
 How to Study Probability with Two Dice and a Spreadsheet - Brightpips05 abril 2025
How to Study Probability with Two Dice and a Spreadsheet - Brightpips05 abril 2025 -
 February Roll and Record With Two Dice by Judy Buckley05 abril 2025
February Roll and Record With Two Dice by Judy Buckley05 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 FIFA Soccer Mod APK 20.1.02 (Unlimited money, coins) Download05 abril 2025
FIFA Soccer Mod APK 20.1.02 (Unlimited money, coins) Download05 abril 2025 -
.png) Alabama State Games05 abril 2025
Alabama State Games05 abril 2025 -
 Teclado Infantil Casio SA-46 para Estudantes e Iniciantes - Koala Music05 abril 2025
Teclado Infantil Casio SA-46 para Estudantes e Iniciantes - Koala Music05 abril 2025 -
 A Plague Tale: Innocence Review - IGN05 abril 2025
A Plague Tale: Innocence Review - IGN05 abril 2025 -
 Jogos de hoje, terça-feira, 12; onde assistir e horários05 abril 2025
Jogos de hoje, terça-feira, 12; onde assistir e horários05 abril 2025 -
 Alan Wakes American Nightmare Table - FearLess Cheat Engine05 abril 2025
Alan Wakes American Nightmare Table - FearLess Cheat Engine05 abril 2025 -
 Download do APK de Jogo de Cozinhar - Bolinhos para Android05 abril 2025
Download do APK de Jogo de Cozinhar - Bolinhos para Android05 abril 2025 -
 Papa's Pizzeria - Net jogos online - jogos grátis05 abril 2025
Papa's Pizzeria - Net jogos online - jogos grátis05 abril 2025 -
 Persona 5 poster de vídeo game anime dos desenhos animados criança05 abril 2025
Persona 5 poster de vídeo game anime dos desenhos animados criança05 abril 2025 -
 How to watch ATP Finals 2022 tennis on TV and live stream05 abril 2025
How to watch ATP Finals 2022 tennis on TV and live stream05 abril 2025